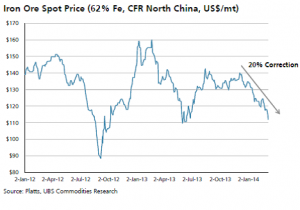
Crisis? What Crisis? The Ukraine-Crimea conflict has to be the most uneventful geopolitical event solely judging by commodities price impact. Energy commodities are showing no price inflation from the Ukraine conflict as China slowdown is more relevant
Brent continues to shrug off any Crimea-Libya concerns and is down 0.8% MTD as the Chinese slowdown is vastly more important.
Russia is going to ship 88 cargoes of Urals crude from Primorsk, UST-Luga and Novorossiysk, highlighting there is no disruption to oil moves.
Spain could replace 10% of Russian gas exports to EU according to Platts. It would be achieved by boosting pipeline gas from Morocco and Algeria, fully utilizing its six regasification terminals to bring LNG and developing its own shale gas resources. However, the EU would pay 50% more if it replaced Russian gas with LNG, Norwegian gas and coal, and 80% more if it did so with renewables, according to Bloomberg and CERA.
China apparent oil demand in January-February fell 1.9% y-o-y, as the Chinese economy weakened. As a result of the shift of Chinese New Year from January in 2013 to February in 2014, apparent oil product demand fell -6.5% in January and rose 3.1% in February. In 2M14, inventory-adjusted demand slid 4.6% y-o-y.
According to Reuters, Libya’s national oil company said on Thursday that protesters had blocked the condensate pipeline linking the al-Wafa field to the Mellitah export complex. The gas pipeline is believed to be still operating. The protesters are reportedly threatening to stop exports from the Mellitah complex which is operated by ENI and NOC.
Coal is flat (-25bps MTD) at $80.50/mt. China announced a new plan to cut coal’s share of energy use to 65.0% in 20141, down from 65.7% in 2013, in a bid to improve air quality in major cities. With total energy consumption growth targeted at 3.2%, coal consumption would rise by just 1.6% this year while supply is expect to grow 3%.
CO2 is seeing another leg down, -28% MTD and moving close to flat on the year (+4.6% YTD), losing almost all the gains seen in the first months from backloading messages from the EU that do not address the chronic oversupply of more than 9 bn mt.
US gas is flat MTD at 4.6/mmbtu after Natural gas storage withdrawal was 57 Bcf. Natural gas storage is now at 896 Bcf, the lowest level since 2003. I expect there to be at least one more storage withdrawal (next week) before the injection season starts. Storage set to peak around 3,625 Bcf, which is approximately 225 Bcf below the 5-year average.
According to LNG World News, the Canadian government has authorised four proposed terminals on the country’s west coast to export LNG. The ministry of natural resources awarded the licences to Pacific Northwest LNG, Prince Rupert LNG, WCC LNG and Woodfibre LNG. Shipments from Canada’s British Columbia province can arrive in Asian ports in just 11 days, or nearly a month sooner than those from the US Gulf coast. All told, these long-term licences allow the four terminals to export up to 73.38m tonnes of LNG per year.
UK gas (NBP) continues to slide, down 8.8% MTD proving Ukraine is no real concern. European gas prices have not moved either, as inventories continue to be well above the 5 year average.
Power prices in Europe decline further: UK at 51.40£/mwh (-2% MTD), Germany at €34.55/mwh (-4% MTD) and Nordpool at €30/mwh (-2.9% MTD).